De-SOx (Semi Dry FGD, Wet FGD)
Solutions for De-sulphur oxide (SOx) are mandatory for several industries in order to abide by the norms of Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change prescribed specially for Thermal Power Plants. One of the most commonly used method for De-sulphur oxide is Flue Gas Desulpharisation (FGD). FGD involves use of a control device that absorbs and remove SOx from the exhaust pipe releasing flue gases using the alkaline reagent or sorbent resulting in formation of solid compound.
Dry/Semi-dry FGD :
Dry/Semi-dry FGD include furnace/duct sorbent injection using sodium/calcium-based reagents, and spray drier absorber technologies using slaked lime or limestone as reagent. In humid environment, the SOx reacts with limestone particles to form sulphite. Dry FGD technology is widely used in small scale industries as those are cost-effective. This technology have SOx reduction efficiency of around 60-90 percent.
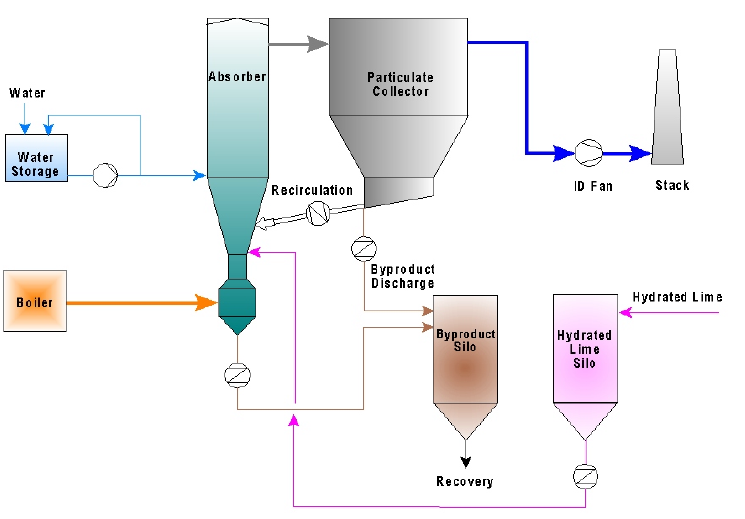
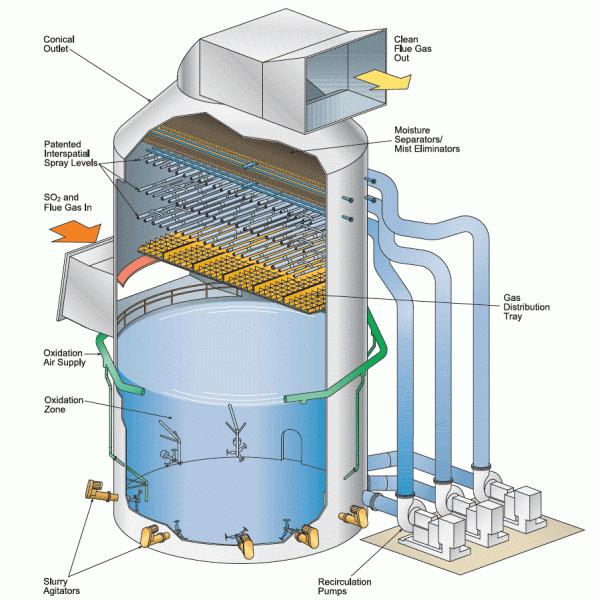
Wet FGD :
Wet FGD is one of the most popularly used de-SOx technology for Indian coal-based power plants. Wet FGD comprises four main processes – flue gas handling, reagent (limestone) handling and preparation, absorption and oxidation, and secondary water and gypsum handling. Limestone-based wet FGD systems can remove 90 to 99 per cent of SOx.
